Product Description
Product Description
| MIC NO. | REF&OEM NO | APPLICATION | YEAR | PHOTO |
| TB34PG9301 | 957726 082990 |
CITROEN BERLINGO / BERLINGO FIRST Box (M_) 1.1 i (MAHDZ, MBHDZ, MBHFX) CITROEN BERLINGO / BERLINGO FIRST Box (M_) 1.4 bivalent CITROEN BERLINGO / BERLINGO FIRST Box (M_) 1.4 i (MBKFX, MBKFW) CITROEN BERLINGO / BERLINGO FIRST Box (M_) 1.4 i bivalent (MBKFW) CITROEN BERLINGO / BERLINGO FIRST MPV (MF_, GJK_, GFK_) 1.1 i (MFHDZ, MFHFX) CITROEN BERLINGO / BERLINGO FIRST MPV (MF_, GJK_, GFK_) 1.4 bivalent CITROEN BERLINGO / BERLINGO FIRST MPV (MF_, GJK_, GFK_) 1.4 i (MFKFX, MFKFW, GJKFWB, GJKFWC, GFKFWC) CITROEN BERLINGO / BERLINGO FIRST MPV (MF_, GJK_, GFK_) 1.4 i bivalent (MFKFW) CITROEN C2 (JM_) 1.1 CITROEN C2 (JM_) 1.4 CITROEN C3 I (FC_, FN_) 1.1 i CITROEN C3 I (FC_, FN_) 1.4 i CITROEN C3 I (FC_, FN_) 1.4 i Bivalent CITROEN C3 II (SC_) 1.1 i CITROEN C3 II (SC_) 1.4 CITROEN C3 Pluriel (HB_) 1.4 CITROEN NEMO Box (AA_) 1.4 CITROEN NEMO Estate 1.4 CITROEN SAXO (S0, S1) 1.1 X,SX CITROEN XSARA (N1) 1.4 i CITROEN XSARA Break (N2) 1.4 i CITROEN XSARA Coupe (N0) 1.4 i FIAT FIORINO Box Body/Estate (225_) 1.4 (225BXA1A, 225BXF1A) FIAT QUBO (225_) 1.4 (225AXA1A) PEUGEOT 1007 (KM_) 1.4 PEUGEOT 106 II (1A_, 1C_) 1.1 i PEUGEOT 206 Hatchback (2A/C) 1.1 PEUGEOT 206 Hatchback (2A/C) 1.1 i PEUGEOT 206 Hatchback (2A/C) 1.4 i PEUGEOT 206 Hatchback (2A/C) 1.4 LPG PEUGEOT 206 Saloon 1.4 PEUGEOT 206 SW (2E/K) 1.1 PEUGEOT 206 SW (2E/K) 1.4 PEUGEOT 206+ (2L_, 2M_) 1.1 PEUGEOT 206+ (2L_, 2M_) 1.4 i PEUGEOT 207 (WA_, WC_) 1.4 PEUGEOT 207 SW (WK_) 1.4 PEUGEOT 306 (7B, N3, N5) 1.1 PEUGEOT 306 (7B, N3, N5) 1.4 SL PEUGEOT 306 Break (7E, N3, N5) 1.4 PEUGEOT 306 Hatchback (7A, 7C, N3, N5) 1.1 PEUGEOT 307 (3A/C) 1.4 PEUGEOT BIPPER (AA_) 1.4 PEUGEOT BIPPER Tepee 1.4 PEUGEOT PARTNER Box (5_, G_) 1.1 PEUGEOT PARTNER Box (5_, G_) 1.4 PEUGEOT PARTNER Box (5_, G_) 1.4 BiFuel PEUGEOT PARTNER Combispace (5_, G_) 1.1 PEUGEOT PARTNER Combispace (5_, G_) 1.4 |
1996-2008 2002-2011 1996-2011 2003-2005 1996-2008 2002-2011 1996-2011 2003-2008 2003-2012 2003-2009 2002- 2002-2571 2002- 2009-2013 2009-2016 2003- 2008- 2009- 1996-2003 1997-2005 1997-2005 1998-2005 2007- 2008- 2005- 1996-2004 1998-2000 1998-2007 1998-2012 2006-2007 2007- 2002- 2002-2007 2009-2013 2009-2013 2006-2013 2007-2012 1994-2001 1994-2001 1997-2002 1993-2001 2000-2003 2008- 2008- 1996-2005 1996-2015 2003-2006 1996-2002 1996-2015 |
Workshop at a Glance
Company Profile
Exhibition Shows
FAQ
Q1: Are you a trading company or manufacturer?
A1: We are industrial and export combination.
Q2: If there’s any quality problem, what would you do to guarantee our rights?
Q2: We seldom get complains from our customers so far. If it really happens, we’ll be responsible for that.
Q3: How long is your delivery time?
Q3: Around 30-45 days if no stock; Around 7 days when stock available.
Q4: What’s your sample policy?
A4: Samples under $50.0 will be no charge, however the freight charge should be borne on buyer’s account.
Normal delivery time will be 4 days when stock available.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Online Technical Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year |
| Car Make: | For GREAT WALL |
| Car Model: | For Berlingo/C2/C3I/II/Nemo1.1/1.4/1.4i |
| Lead time: | 60-90 days |
| OEM service: | Available |
| Samples: |
US$ 15/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

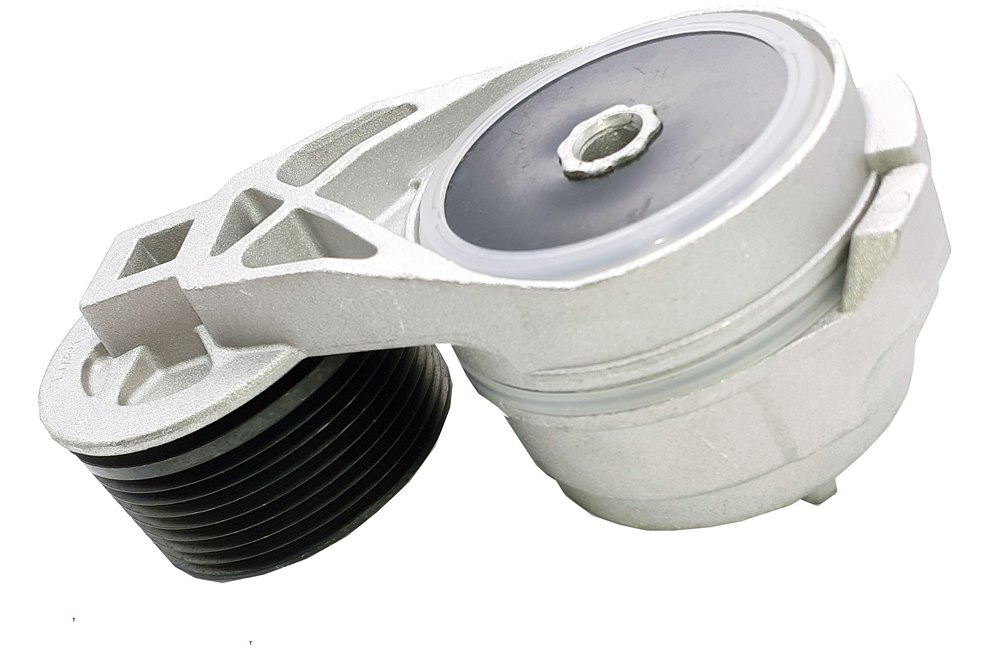
What are the reliability and durability aspects of drive belt tensioners in ensuring consistent tension?
Reliability and durability are crucial aspects of drive belt tensioners in ensuring consistent tension within a vehicle’s belt system. Drive belt tensioners play a vital role in maintaining the proper tension of the drive belt, which is essential for reliable power transmission and preventing belt slippage. Here’s a detailed explanation of the reliability and durability aspects of drive belt tensioners in ensuring consistent tension:
- Material Selection:
- Design and Engineering:
- Load and Tension Capacity:
- Resistance to Environmental Factors:
- Maintenance and Service Life:
The choice of materials used in manufacturing drive belt tensioners significantly impacts their reliability and durability. Tensioners are typically constructed using high-strength materials such as steel, aluminum, or reinforced polymers. These materials provide the necessary strength, rigidity, and resistance to wear and fatigue. The selected materials should be able to withstand the forces and loads experienced during operation without deformation or premature failure, ensuring long-term reliability and consistent tensioning performance.
The design and engineering of drive belt tensioners are critical factors in ensuring their reliability and durability. Tensioners need to be designed to accommodate the specific requirements of the belt system and driven components. This includes considerations such as belt routing, tensioner mounting, and the integration of features like pulleys, bearings, and damping mechanisms. Well-designed tensioners undergo rigorous testing and analysis to ensure they can withstand the anticipated loads, vibrations, temperature variations, and other operating conditions. Proper engineering practices contribute to the longevity and consistent performance of the tensioner throughout its service life.
Reliability and durability of drive belt tensioners are closely linked to their load and tension capacity. Tensioners must be capable of applying and maintaining the proper tension on the drive belt, ensuring it remains properly engaged with the pulleys. The tensioner should be designed with a suitable load capacity to handle the anticipated forces and loads imposed on the belt system during various operating conditions. Adequate load and tension capacity prevent excessive belt deflection, slippage, or premature wear, ensuring consistent tension and reliable power transmission.
Drive belt tensioners are exposed to various environmental factors that can impact their reliability and durability. Factors such as temperature variations, moisture, dirt, and chemical exposure can affect the performance and lifespan of the tensioner. To ensure consistent tension, tensioners are often designed with protective coatings, seals, or materials that offer resistance to these environmental elements. Proper sealing and corrosion-resistant materials minimize the risk of contamination or degradation, ensuring the tensioner’s long-term reliability and consistent tensioning capability.
Regular maintenance and adherence to recommended service intervals are essential for preserving the reliability and durability of drive belt tensioners. Tensioners should be inspected periodically for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Proper lubrication of moving parts, such as pulleys and bearings, is also crucial for their longevity and consistent performance. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance procedures and replacing worn or damaged tensioners in a timely manner helps ensure that the tensioner maintains its reliability and consistent tensioning function throughout its expected service life.
In summary, the reliability and durability aspects of drive belt tensioners are crucial in ensuring consistent tension within a vehicle’s belt system. Material selection, design and engineering practices, load and tension capacity, resistance to environmental factors, and proper maintenance all contribute to the reliability and longevity of tensioners. By choosing well-designed and properly maintained tensioners, automotive systems can benefit from consistent belt tension, reliable power transmission, and minimized risks of belt slippage or failure.

How do innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology impact their use in modern vehicles?
Innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology have significantly impacted their use in modern vehicles, leading to improved performance, reliability, and overall efficiency. These advancements have resulted in the development of more sophisticated and efficient tensioner designs that address the evolving needs of modern automotive systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology impact their use in modern vehicles:
- Enhanced Belt Control:
- Increased Durability:
- Improved Efficiency:
- Integration with Advanced Systems:
- Diagnostic Capabilities:
New technologies and innovations have allowed for improved belt control in modern drive belt tensioners. Tensioners now feature advanced damping mechanisms, such as hydraulic or pneumatic dampers, that help minimize belt vibrations and reduce noise. These innovations result in smoother operation and increased comfort for vehicle occupants. Additionally, advancements in tensioner design have improved the ability to maintain consistent belt tension over a wide range of operating conditions, ensuring optimal power transmission and reducing the risk of belt slippage.
Advancements in materials, manufacturing techniques, and engineering have led to increased durability and longevity of drive belt tensioners. Modern tensioners are often constructed using high-strength materials, such as reinforced polymers or advanced metals, that can withstand higher loads and resist wear and fatigue. This increased durability means that tensioners can reliably operate for longer periods between maintenance or replacement intervals, reducing the overall cost of ownership and improving the reliability of the vehicle.
Innovations in drive belt tensioner technology have contributed to improved efficiency in modern vehicles. Tensioners now incorporate features like automatic tension adjustment or self-adjusting mechanisms that optimize belt tension based on operating conditions. This ensures that the belt is neither too loose nor too tight, reducing energy losses due to belt slippage or excessive drag. By maintaining the optimal tension, modern tensioners help improve the efficiency of driven components, such as the alternator or air conditioning compressor, resulting in reduced fuel consumption and improved overall vehicle efficiency.
Modern vehicles often incorporate advanced systems and components that rely on the drive belt system, such as hybrid powertrains or electrically driven accessories. Innovations in tensioner technology have facilitated the integration of these advanced systems by accommodating the additional requirements and loads. For example, tensioners designed for hybrid vehicles may incorporate features to handle the higher forces associated with electric motor assistance. This integration ensures proper operation and reliability of the entire system, allowing for the seamless functioning of modern automotive technologies.
Some modern drive belt tensioners are equipped with diagnostic capabilities that can monitor their performance and detect potential issues. These advanced tensioners may include sensors or integrated electronic modules that can provide real-time data on belt tension, temperature, or other parameters. This information can be utilized by the vehicle’s onboard diagnostic systems to alert the driver or service technician of any abnormalities or impending failures. Diagnostic capabilities enhance the overall maintenance and reliability of the tensioner system, allowing for proactive repairs or replacements before major failures occur.
In summary, innovations and advancements in drive belt tensioner technology have had a profound impact on their use in modern vehicles. Enhanced belt control, increased durability, improved efficiency, integration with advanced systems, and diagnostic capabilities are some of the key benefits resulting from these advancements. As automotive systems continue to evolve, drive belt tensioners will likely continue to be refined and optimized to meet the demands of modern vehicles, ensuring efficient power transmission, reduced maintenance requirements, and improved overall performance.
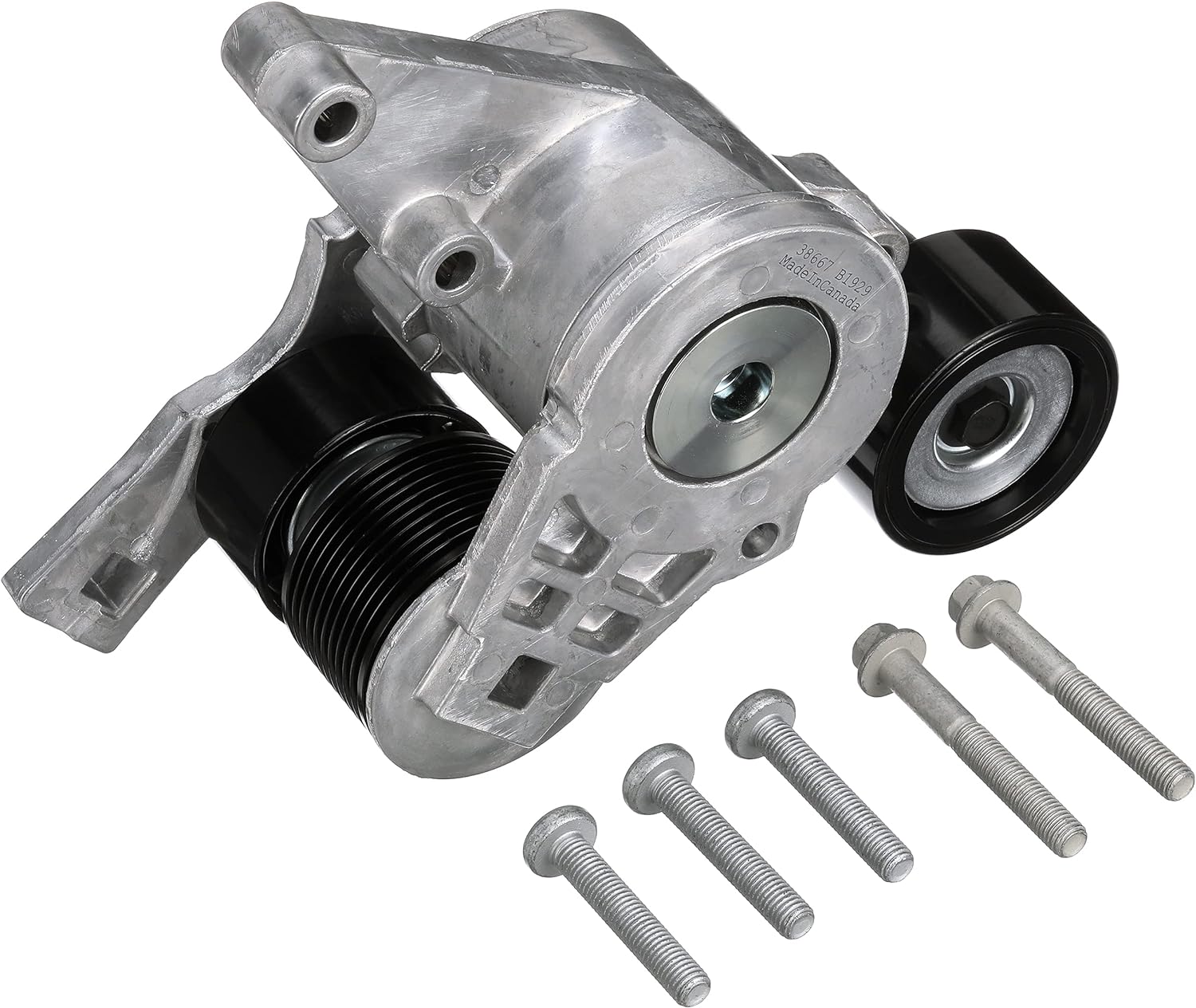

In what automotive applications are drive belt tensioners commonly used for optimal performance?
Drive belt tensioners are commonly used in various automotive applications to ensure optimal performance and reliability. These tensioners play a crucial role in maintaining proper belt tension, which is essential for efficient power transmission and the operation of different vehicle systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of the automotive applications where drive belt tensioners are commonly used:
- Engine Systems:
- Power Steering Systems:
- Air Conditioning Systems:
- Water Pump Systems:
- Other Auxiliary Systems:
Drive belt tensioners are extensively employed in engine systems to maintain the tension of the accessory drive belt. The accessory drive belt, also known as the serpentine belt, connects various engine-driven components such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. The tensioner ensures that the belt remains properly tensioned, allowing efficient power transfer to these components. By maintaining the optimal tension in the accessory drive belt, the tensioner contributes to the proper functioning of the engine’s auxiliary systems.
In power steering systems, drive belt tensioners are commonly used to maintain proper tension in the power steering belt. The power steering belt connects the power steering pump to the engine’s crankshaft or other pulleys. The tensioner helps to keep the power steering belt at the correct tension, ensuring smooth and responsive power steering operation. By maintaining optimal belt tension, the tensioner allows the power steering system to assist in steering maneuvers effectively.
Drive belt tensioners are also utilized in air conditioning systems to maintain tension in the air conditioning compressor belt. The compressor belt drives the air conditioning compressor, which is responsible for circulating refrigerant and cooling the vehicle’s interior. The tensioner ensures that the compressor belt remains properly tensioned, allowing efficient power transfer to the compressor. This ensures the reliable operation of the air conditioning system, allowing it to provide effective cooling and climate control.
Drive belt tensioners are commonly employed in water pump systems to maintain tension in the water pump belt. The water pump belt connects the engine’s crankshaft or other pulleys to the water pump, which circulates coolant throughout the engine to prevent overheating. The tensioner ensures that the water pump belt remains properly tensioned, allowing efficient power transfer to the water pump. This helps maintain the proper cooling of the engine, contributing to its optimal performance and preventing overheating.
Drive belt tensioners can also be found in various other auxiliary systems in vehicles. For example, they may be used in systems such as the air injection pump, which helps reduce emissions, or the smog pump, which aids in the control of exhaust emissions. These tensioners ensure that the belts driving these auxiliary components remain properly tensioned, enabling efficient operation and optimal performance of these systems.
In summary, drive belt tensioners are commonly used in automotive applications such as engine systems, power steering systems, air conditioning systems, water pump systems, and other auxiliary systems. By maintaining proper belt tension, these tensioners contribute to the efficient power transmission and reliable operation of various vehicle components and systems, ensuring optimal performance and functionality.


editor by CX 2024-04-25
China supplier CZPT CZPT Engine Spare Parts Vg2600060313 Wd615 Pulley Tensioner a 3-axle vehicle
Product Description
| After-sales Service: | Yes |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Yes |
| Type: | Engine Bearing |
| Material: | Stainless Steel |
| Tolerance: | P4 |
| Certification: | ISO9001 |
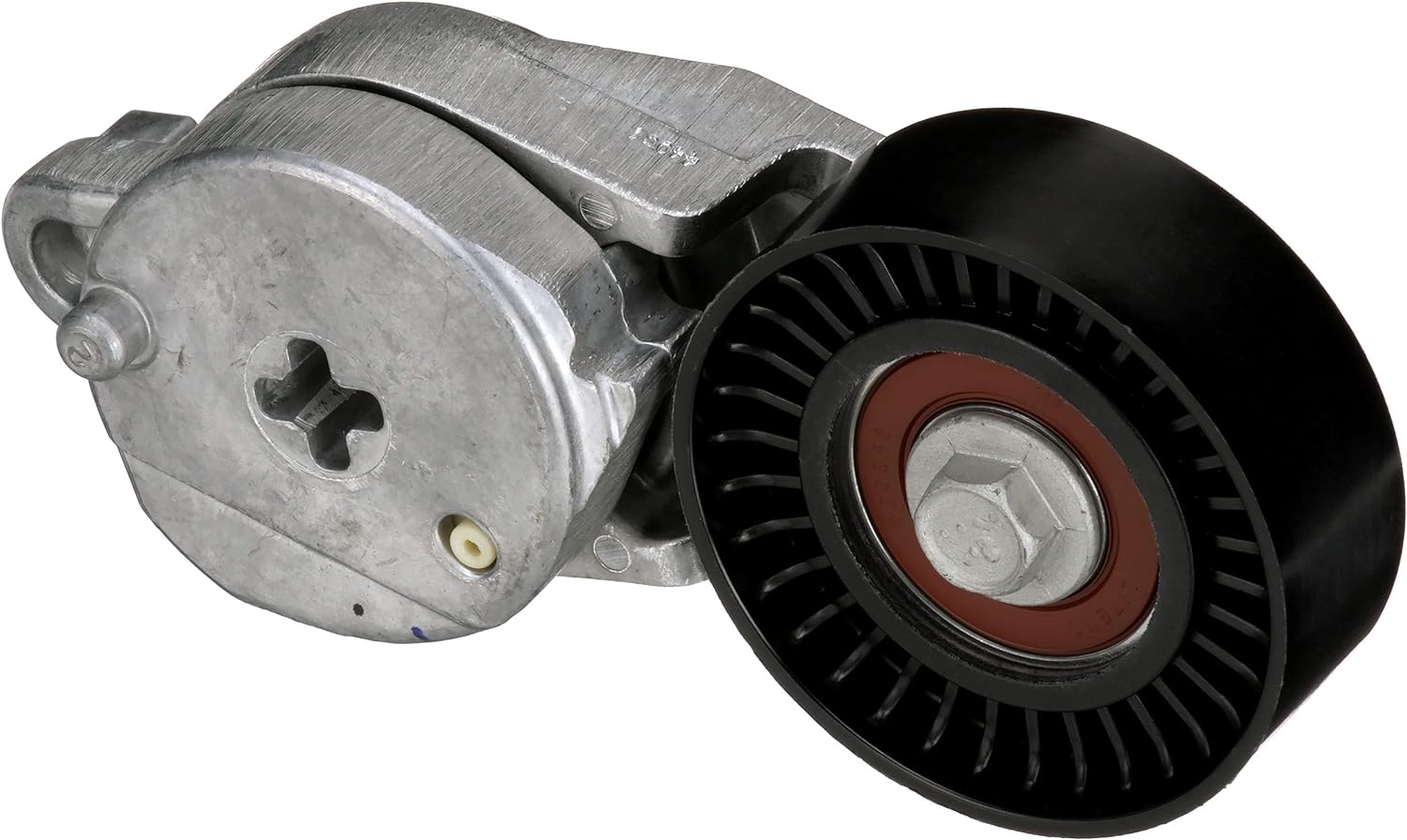

What role do materials and coatings play in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners?
Materials and coatings play a crucial role in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners. The selection of appropriate materials and the application of suitable coatings contribute to the overall durability, reliability, and functionality of the tensioners. Here’s a detailed explanation of the role that materials and coatings play in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners:
- Material Selection:
- Coatings and Surface Treatments:
- Corrosion-resistant Coatings: Tensioners are often exposed to moisture, chemicals, and other corrosive elements. Applying corrosion-resistant coatings, such as zinc plating or electrocoating, helps protect the tensioner from rust and corrosion, extending its lifespan.
- Lubricious Coatings: Coatings with low friction properties, such as PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) or molybdenum disulfide, can be applied to reduce friction between the tensioner and the drive belt. This helps minimize wear and heat generation, enhancing the tensioner’s performance and longevity.
- Wear-resistant Coatings: Tensioners can experience wear due to constant contact and friction with the drive belt. Applying wear-resistant coatings, such as hard chrome or ceramic coatings, can increase the tensioner’s resistance to wear and extend its service life.
- Noise and Vibration Damping Coatings: Some coatings, such as rubberized or elastomeric coatings, can provide noise and vibration damping properties. These coatings help reduce noise and vibrations generated by the tensioner, improving overall drive system performance and passenger comfort.
- Impact on Performance:
- Longevity and Reliability:
The choice of materials used in manufacturing drive belt tensioners is critical for their performance and longevity. Tensioners are typically constructed using high-strength materials such as steel, aluminum, or reinforced polymers. These materials provide the necessary strength, rigidity, and resistance to wear and fatigue. The selected materials should have sufficient tensile strength to withstand the forces and loads experienced during operation without deformation or premature failure. Using high-quality materials ensures that the tensioners can maintain the desired tension level and resist wear, contributing to their long-term performance and longevity.
Coatings and surface treatments applied to drive belt tensioners offer several benefits for their performance and longevity. These coatings provide protection against environmental factors, reduce friction, and enhance the durability of the tensioners. Some common coating options include:
The choice of materials and coatings directly affects the performance of drive belt tensioners. Suitable materials with high strength and durability ensure that the tensioner can withstand the forces and loads imposed during operation without failure or excessive deflection. Coatings and surface treatments minimize friction, wear, and corrosion, optimizing the tensioner’s performance and ensuring consistent tensioning capability. By reducing friction and wear, materials and coatings can also contribute to improved power transmission efficiency and reduced energy losses in the belt drive system.
The use of appropriate materials and coatings enhances the longevity and reliability of drive belt tensioners. Proper material selection and the application of protective coatings extend the tensioner’s service life by minimizing wear, corrosion, and degradation. Materials and coatings that resist environmental factors and maintain their performance characteristics over time ensure the longevity and reliability of the tensioner, reducing the risk of premature failure or the need for frequent replacements.
In summary, materials and coatings play a vital role in the performance and longevity of drive belt tensioners. The selection of high-quality materials with adequate strength and the application of suitable coatings contribute to the tensioner’s durability, reliability, and functionality. Coatings provide protection against corrosion, reduce friction, minimize wear, and can even dampen noise and vibrations. By ensuring proper materials and coatings, drive belt tensioners can maintain optimal performance, provide consistent tensioning, and have an extended service life.

Can you explain the principles behind the operation and adjustment of drive belt tensioners?
The operation and adjustment of drive belt tensioners are based on specific principles that ensure the proper tension of the drive belt in automotive applications. Understanding these principles is crucial for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of the belt system. Here’s a detailed explanation of the principles behind the operation and adjustment of drive belt tensioners:
- Tensioner Design:
- Automatic Tensioning:
- Tensioner Pulley Movement:
- Tension Adjustment:
- Tensioner Maintenance:
Drive belt tensioners are typically designed as spring-loaded or hydraulic devices. Spring-loaded tensioners utilize a spring mechanism that applies force to the tensioner pulley, keeping the belt at the desired tension. Hydraulic tensioners, on the other hand, use hydraulic pressure to control the tensioner pulley and maintain the belt tension. The design of the tensioner ensures that it can compensate for belt elongation and maintain the correct tension throughout the life of the belt.
Drive belt tensioners are designed to automatically adjust the tension of the belt as it wears or stretches over time. The tensioner continuously monitors the tension of the belt and compensates for any changes to maintain the desired tension. This automatic adjustment is crucial because the tension requirements of the belt can vary depending on factors such as engine speed, temperature, and load conditions. Automatic tensioning ensures that the belt remains properly tensioned under different operating conditions.
Drive belt tensioners operate by controlling the movement of the tensioner pulley. The tensioner pulley is mounted on a pivot, allowing it to move in response to changes in belt tension. When the belt tension increases, the tensioner pulley moves to maintain the proper tension. Conversely, if the tension decreases, the tensioner pulley adjusts to increase the tension. This movement is achieved through the action of the spring or hydraulic mechanism within the tensioner, which applies the necessary force to the tensioner pulley.
Adjusting the tension of a drive belt typically involves manually adjusting the position of the tensioner or its components. The exact method of adjustment can vary depending on the specific design of the tensioner and the vehicle. Some tensioners have a manual adjustment bolt or mechanism that allows for fine-tuning of the tension. In other cases, adjusting the belt tension may involve loosening the tensioner mounting bolts, moving the tensioner to the desired position, and then tightening the bolts. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and specifications for proper tension adjustment.
Proper maintenance of drive belt tensioners is essential for their reliable operation. Regular inspection of the tensioner and associated components helps identify signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. If any issues are detected, the tensioner may need to be replaced or adjusted accordingly. Additionally, it is important to ensure that the tensioner is properly lubricated if it has lubrication points specified by the manufacturer. Adequate lubrication helps maintain smooth operation and prevents premature wear of the tensioner components.
In summary, the principles behind the operation and adjustment of drive belt tensioners involve the design of the tensioner mechanism, automatic tensioning to compensate for belt elongation, control of tensioner pulley movement, manual tension adjustment methods, and proper maintenance practices. Understanding these principles enables proper tensioning of the drive belt, ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of the belt system in automotive applications.
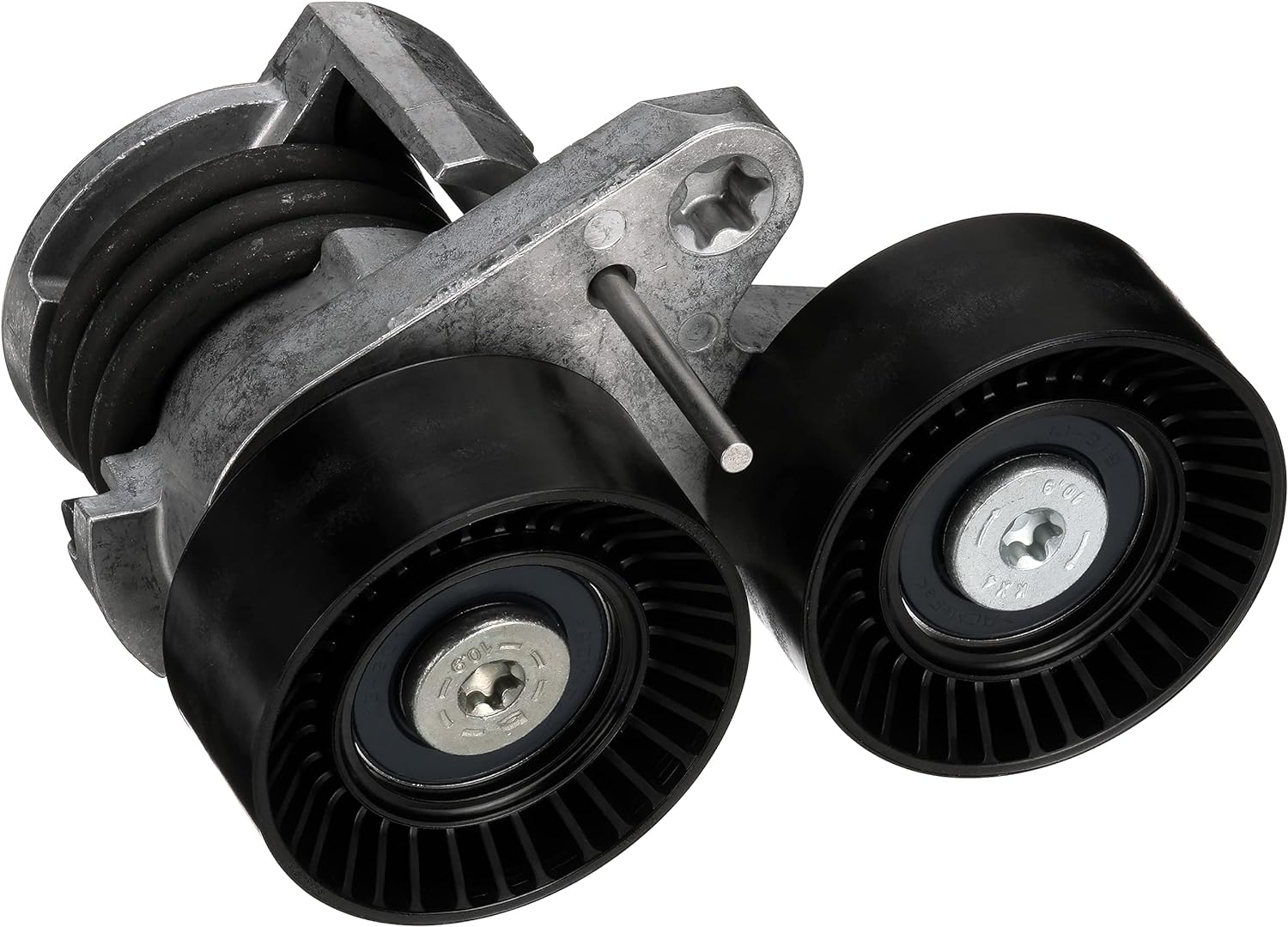

Can you describe the various types of drive belt tensioners, such as automatic or spring-loaded tensioners?
Drive belt tensioners come in various types, each with its own design and mechanism for maintaining belt tension. These types include automatic tensioners, spring-loaded tensioners, and hydraulic or dampened tensioners. Here’s a detailed description of each type:
- Automatic Tensioners:
- Spring-Loaded Tensioners:
- Hydraulic or Dampened Tensioners:
Automatic tensioners are commonly used in modern automotive systems. They utilize a combination of mechanical components and springs to automatically adjust and maintain the proper tension in the drive belt. Automatic tensioners typically consist of a spring-loaded arm or pulley that applies tension to the belt. As the belt stretches due to wear or temperature changes, the tensioner compensates by applying more force, ensuring optimal tension at all times. The automatic tension adjustment feature of these tensioners eliminates the need for manual adjustment and provides convenience and consistent belt tension.
Spring-loaded tensioners are another common type of drive belt tensioners. They rely solely on mechanical springs to apply and maintain tension in the drive belt. Spring-loaded tensioners consist of a pulley mounted on an arm that is loaded with a strong spring. The spring applies a specific amount of force to the pulley, which in turn maintains tension in the belt. These tensioners usually have a fixed tension setting determined by the design of the spring, and manual adjustment is typically not required. Spring-loaded tensioners are widely used in various automotive applications and provide consistent tension over time.
Hydraulic or dampened tensioners are a type of tensioner that utilizes hydraulic fluid or a dampening mechanism to maintain belt tension. These tensioners often consist of a pulley connected to a hydraulic cylinder or a dampening mechanism such as a torsion bar. The hydraulic or dampening mechanism allows for controlled movement of the pulley, absorbing vibrations and fluctuations in the belt tension. This type of tensioner provides smoother operation, reduces noise, and prolongs the life of the belt and associated components. Hydraulic or dampened tensioners are commonly used in applications where noise and vibration reduction are important, such as in luxury vehicles.
In summary, there are several types of drive belt tensioners, including automatic tensioners, spring-loaded tensioners, and hydraulic or dampened tensioners. Automatic tensioners use mechanical components and springs to automatically adjust belt tension, spring-loaded tensioners rely on mechanical springs for tension maintenance, and hydraulic or dampened tensioners utilize hydraulic or dampening mechanisms to provide smoother operation and reduce noise. The choice of tensioner type depends on the specific application, performance requirements, and design considerations of the automotive system.


editor by CX 2024-04-16
China Good quality Auto Parts Timing Belt Idler Pulley OEM 1340513 1340535 93297272 Vkm35002 Apv2122 532010910 for Opel Senator Astra Combo CZPT a Tigra with Free Design Custom
Product Description
Quick view:
| Description | Auto Parts Timing Belt Idler Pulley OEM 134571 134571 93297272 VKM35.05 For INA: F-11571 For INA: F-218179 For INA: F-224134 For INA: F-224134.BSR For SKF: VKM 35 |
Kia | ||
| B660-12-7 | Mazda | |||
| RFC6-12-7 | Mazda | |||
| F801-12-7 | Mazda | |||
| FE1H-12-7 | Mazda | |||
| WL01-12-7 | Mitsubishi | |||
| MD315265 | VKM75 | Mitsubishi | ||
| 24410-26 | Mitsubishi | |||
| MD169592 | VKM75 | Mitsubishi | ||
| MD115976 | VKM75044 | CR5073 | F-554646 | Mitsubishi |
| MD182537 | VKM75064 | CR5078 | Mitsubishi | |
| MD030605 | VKM751 | Mitsubishi | ||
| MD129355 | VKM75101 | CR5070 | Mitsubishi | |
| 23357-32040 | VKM75113 | CR5071 | F-124078 | Hyundai |
| MD | Mitsubishi | |||
| MD129033 | VKM75130 | CR5084 | Mitsubishi | |
| 24450-33571 | VKM75144 | CR5067 | Hyundai | |
| 23357-42571 | VKM75601 | CR5076 | F-124070 | Hyundai |
| 24317-42571 | VKM75612 | CR5077 | F-124052 | Hyundai |
| 24317-42571 | VKM75612 | CR5077 | F-124052 | Hyundai |
| MD352473 | VKM75613 | CR5171 | Mitsubishi | |
| MD329976 | VKM75615 | CR5172 | Mitsubishi | |
| MD320174 | VKM75616 | CR5137 | Mitsubishi | |
| 24410-57150 | VKM75621 | CR5225 | Hyundai | |
| MD356509 | VKM75625 | CR5206 | Mitsubishi | |
| 12810-71C02 | VKM76 | SUZUKI | ||
| 12810-81401- | SUZUKI | |||
| 12810-86501 | VKM76203 | CR5101 | SUZUKI | |
| 13505-87702- | S ubaru | |||
| 8-94472-349- 1 |
VKM79.1 | Daewoo | ||
| 13503-62030 | VKM81 | Toyota | ||
| 13503-54571 | VKM81 | Toyota | ||
| 13503-54030 | VKM81 | Toyota | ||
| 13503-10571 | VKM81201 | CR5026 | F-124073 | Toyota |
| 13503-1571 | VKM81203 | CR5571 | F-124089 | Toyota |
| 13503-11040 | VKM814 | Toyota | ||
| 13074-05E | Nissan | |||
| 13077-V7202 | VKM825 | Nissan | ||
| FS01-12-730A | VKM84 | Mazda | ||
| FE1H-12-730A | VKM846 | Mazda | ||
| OK972-12-730 | VKM84601 | CR5055 | Kia | |
| 24810-33571 | VKM85 | I suzu | ||
| 9281571212 | CR3395 | F-22 | Fiat / Lancia | |
| 57119243L | VKM11107 | CR3467 | F-55571 | Audi / VW |
| 1112571119 | VKM23063S | CR1458 | F-220122 | Mercedes Benz |
| CR3416 | PSA | |||
| 7784613 | CR1440P | F-123753 | Fiat / Lancia | |
| CR1452P | Fiat / Lancia | |||
| 601257170 | CR1477 | F-220124 | Mercedes Benz | |
| CR1478 | ||||
| CR1480 | O pel / GM | |||
| CR1480P | O pel / GM | |||
| 715713 | CR1481 | FORD | ||
| CR1484 | Fiat / Lancia | |||
| 90324097 | CR1486 | F-225717 | O pel / GM | |
| CR1497 | Fiat / Lancia | |||
| CR1498 | Fiat / Lancia | |||
| CR1499 | FORD | |||
| 7301662 | CR1647 | F-88019.2 | Fiat / Lancia | |
| 11281731220 | CR3571 | F-225569 | BMW | |
| 11281731838 | CR3571 | F-225633 | BMW | |
| XS4Q6B217AD | CR3102 | F-143 | FORD | |
| 6682571419 | CR3118 | Mercedes Benz | ||
| 668257171 | CR3119 | Mercedes Benz | ||
| 9635638380 | CR3218 | F-123183.18 | R enault | |
| 46547564 | CR3270 | Fiat / Lancia | ||
| 5 | Fiat / Lancia | |||
| 96036288 | CR3276 | F-120676 | PSA | |
| 962 | PSA | |||
| CR3296 | F-123788 | PSA |
ZheJiang Mighty (SI Bearing)are providing deep groove ball bearing, tapered roller bearing, pillow block bearing, spherical roller bearing, angular contact ball bearing, needle bearing, self-aligning ball bearing, linear bearing, wheel hub bearing, hub unit, clutch release bearing, belt tensioner, etc.
Our Bearing Advantage:
1.Free Sample bearing
2.ISO certified
3.Bearing Small order accepted
4.In Stock bearing
5.OEM bearing service
6.Professional: Over 20 years manufacture bearing
7.Customized bearing, Customer’s bearing drawing or samples accepted
8.Competitive price
9.TT Payment, Paypal, Alibaba payment, Trade Assurance Order
FAQ:
Q: Can you help with my own brand?
A: Sure. We can make for your brands. We can mark your brand name and use your box’s design with the legal authority letter.
Q: How can I make an inquiry?
A: You can contact us by email, telephone, WhatsApp, , etc.
Q: How long can reply inquiry?
A: Within 24 hours.
Q: Which Service you can provide?
A: 1. Help customers to choose correct bearing
2. Professional team, make your purchase easily
Q: When are you going to deliver?
A: Sample: 5-15 business days after payment is confirmed.
Bulk order:15-60 workdays after deposit received…
Q: What’s your delivery way?
A: By sea, by air, by train, express as your need.
Q: What are your terms of delivery?
A: EXW, FOB, CFR, CIF, DAP, etc.
Q: Can you support the sample order?
A: Yes, we can supply the sample if we have parts in stock, but the customer has to pay the sample payment(according to the value of the samples) and the shipping cost.
Q: What are you going to do if there has a claim for the quality or quantity missing?
A: 1. For quality, during the warranty period, if any claim for it, we shall help customer to find out what’s the exactly problem. Using by mistake, installation problem, or poor quality? Once it’s due to the poor quality, we will arrange the new products to customers.
2. For missing quantities, there have 2 weeks for claiming the missing ones after receiving the goods. We shall help to find out where it is.
Types of V-Belt Drives
When evaluating drive technologies, you might want to consider a V-Belt. Not only can it improve the performance of an older drive, but it can save you time and money in the long run. Industry standard V-belts are prone to failing because of excessive wear, heat cracks, and stretching. Inefficient and downtime resulting from frequent retensioning and replacement can cost your company both time and money.
Cross-
A cross-belt for a V-Belt is a belt that is used in a conveyor system. This belt consists of 2 parts: an elastomer core and a fabric cover. The elastomer core is typically made of high-shock-resistant polyurethane. Different manufacturers have different synthetic rubber stocks, which may be used to prevent premature failure and extend the operating temperature range of the belt. Ideally, a well-engineered V-belt is stiff in the width and flexible along the length of the belt. The fabric covers are generally made of 2 different types of rubber, including compression and cushion rubber.
The diameter of the driver and driven pulleys are important considerations for choosing the right cross-belt for a V-belt. This will determine the belt length. The length should be proportional to the diameter of the drive shaft. Smaller diameters are better for smaller belts, which can increase elongation, which decreases the life of the belt. Larger diameters, on the other hand, can increase slippage, fluctuating force, and power loss.
Choosing the right V-belt for your vehicle is important, especially if you’re replacing a worn-out one. In some cases, the old V-belt may become too loose or a loop with a rubber-coated edge. You should measure the length of the belt before you buy it. Using a flexible english measuring tape, you can determine which size is best for your vehicle.
A cross-belt can increase power transmission by minimizing slipping. It also provides shock-absorption and increases the load capacity of the V-belt. It is the best option for heavy-duty machines where torque and power are critical. In some applications, this belt may be more effective than an open belt. If you use it for short distances, a cross-belt can be a better choice.
When choosing a V-belt, make sure to check the power ratio. The power of a belt depends on the initial tension applied to it. Also, the friction between the 2 mating surfaces is a factor. A V-belt with a high power density is not suitable for close-center applications. You can choose a narrow V-belt if you need a narrow belt for your machine.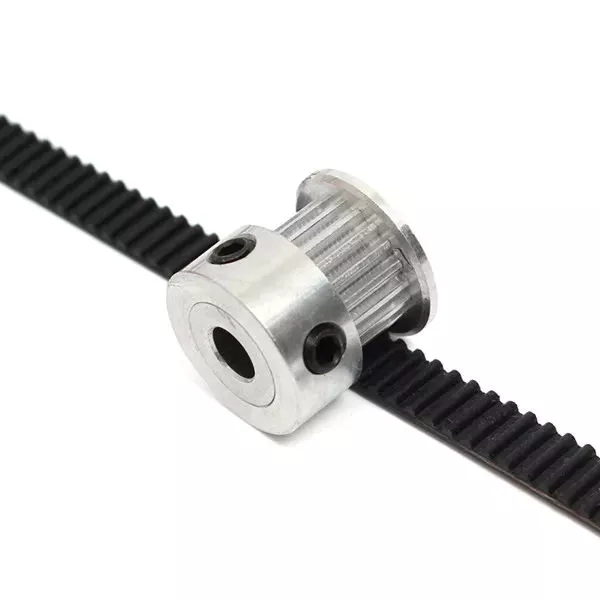
U-shaped
The V-belt is a versatile belt used in countless industrial applications. Advancements in engineering have led to many different types of V-belts. Whether it’s a U-shaped belt or a double-sided V-belt, proper installation and maintenance are crucial for trouble-free operation. Below are some common V-belt specifications. Read on to learn more! The U-shaped V-belt is 1 of the most common.
A V-belt is a flexible, pliable machine element used to transmit power between 2 or more rotating shafts. Its cross-section is trapezoidal, so that as the tension increases on 1 side, the belt wedges into the groove on the opposite side. The increased friction between the 2 components results in a high torque transmission and minimal power loss from slippage. U-shaped V-belts are ideal for a variety of applications, from lawn mowers to cars.
The U-shaped V-belt is made of 2 parts: an elastomer core and a textile cover. The core is made from a flexible material with high flexural strength and shock resistance. The cover is made of textile material that is treated to create a chemical bond with the belt’s core material. This makes it pliable and strong while preventing the cover from becoming worn out or damaged.
Unlike flat belts, U-shaped V-belts are designed to fit into a U-shaped sheave, which increases their lateral rigidity. They also maintain their stability under shock and vibration loads. Their simplicity makes installation and tensioning much easier. The constructional components of a standard V-belt are illustrated in Figure 9. Each component has a vital role in the belt’s performance. Similarly, different materials can influence the belt’s performance.
As with any belt, proper tension is crucial. Having a loose belt causes slippage and rapid wear, which robs you of energy and productivity. Likewise, too much tension can cause premature belt wear. Proper tension is defined as the lowest level at which the belt does not slip or squeal under peak load. This tension range can still operate a drive, so it’s important to find the correct tension for your particular application.
Cogged
There are many advantages of a Cogged V-Belt. Its extra-thick construction allows for bends around smaller pulleys. It also runs cooler and lasts longer than a traditional V-belt. In addition, it has a higher coefficient of friction than a wrapped V-belt. Cogged V-Belts can also resist heat, making them an excellent choice for high-temperature applications.
A cogged V-Belt is also less likely to suffer from heat buildup, which can shorten the life of a standard belt and increase downtime and replacement costs. A Cogged V-Belt is more expensive than a wrap-molded belt, but it will pay for itself in as little as 1 month. Most synchronous belt conversions pay for themselves in less than 2 years. A longer payback time is typical with a larger system.
Cogged V-Belts are used in many applications, including in-line conveyors, gantry cranes, and wind turbines. The belt itself is composed of various types of rubber and reinforcements. They undergo tensile and compressive stresses as each segment of the belt passes through the pulley. Therefore, a different type of material is needed for the bottom side of the belt. The ideal material for this area should have a high coefficient of friction and increased wear resistance.
The Cogged V-Belt has a trapezium-shaped cross-section. The fabric cover resists heat and abrasion and helps protect the internal components of the v-belt. The different types of materials used in the fabric cover are patented. In some cases, the fabric cover is made of Kevlar or aramid fiber. This allows for smaller pulley diameters and more flexibility.
A Cogged V-Belt is made of 2 pieces of material. One is thick and includes a pitch line while the other has a slack side. The top is thicker and wider, while the bottom side has a lower pitch line. The slack side has a less pitch and more tension. Using a Cogged V-Belt will increase your productivity and help you save money.
Wedge
The Wedge V-Belt is 1 of the most popular types of drive belts available. The patented, narrow-profile design allows for lighter, thinner belts with greater transmission capabilities. The HY-T V-Belt is constructed with Vytacord tension members for strength and dimensional stability, and includes a cushion made of engineered rubber compound. This belt is ideal for high-speed, high-resistance applications, such as compressors, stone mills, and centrifugal pumps.
HY-T CZPT(r) belts have a continuous V-section, and a wide angle of flexibility. They provide torsional rigidity in long-center drives and are resistant to oil. The CZPT(r) belt is available in lengths up to 140 inches. Its free ribs wedge into the sheave groove to reduce belt whipping. This belt is also designed to fit into new designs and applications, so it’s compatible with virtually any type of drive.
The Wedge V-Belt is a popular choice in industrial applications. Its narrow profile reduces drive weight and space, allowing for higher horsepower. In addition, it can carry a higher load than a standard V belt. Its low cost and high efficiency make it a popular choice for many industrial applications. In addition to industrial settings, it is a popular choice in automotive and construction applications. While it may seem like a complicated belt design, the Wedge V-Belt is ideal for industrial use.
Wedge V-Belts have the same contact angle as the traditional v-belt, but have a narrow upper width. Their narrower upper width decreases their weight, which equalizes the tension on the tensile cord. The wedge-shaped design improves grip and increases wedge effect. Its durability is excellent, and it also features a cog shape for greater gripping power.
Wedge V-Belts are an efficient way to transmit power between 2 drives. They can move significant loads and can achieve very high speeds. The wedged shape of the belt allows it to wedge into the groove when the load increases. Moreover, it minimizes power loss due to slippage. If you want to get the most out of a Wedge V-Belt, make sure it is made of a material that resists heat and moisture.


China OEM a 000 202 00 19 Auto Guid Pulley for Mercedes-Benz wholesaler
Product Description
Product spections :
| Interchange number: | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| A |
Description :
1. The tensioner is a belt tensioner used in the automobile transmission system. The tension pulley is mainly composed of a fixed shell, a tension arm, a wheel body, a torsion spring, a rolling bearing and a spring sleeve. It can automatically adjust the tension force according to the different tightness of the belt to make the transmission system stable, safe and reliable.
2. The main function of the tensioner bearing is to support the mechanical rotating body.
3.Reduce the friction coefficient during its movement and ensure its rotation accuracy.
4.Change sliding friction into rolling friction.
| CHRYSLER | 0571 2836AA |
| CHRYSLER | 68571888AA |
| CHRYSLER | K68571888AA |
| MERCEDES-BENZ | 2722571819 |
| MERCEDES-BENZ | 057120019 |
| MERCEDES-BENZ | A057120019 |
| MERCEDES-BENZ | A05712571 |
| MERCEDES-BENZ | 05712571 |
| VAG | 57103341A |
What Is a V-Belt?
What is a v-belt? It is a rubber belt that is trapezium-shaped and has an elastomer core that holds the parts together. Its elastomer core is generally made of polyurethane and has good shock resistance and flexural strength. V-belts sometimes have 2 sections, 1 of which is a compression rubber and the other cushion rubber. They can be narrow or wide, depending on their use.
Classical V-belts replace leather belts
Classical V-belts are a popular choice among truck drivers because they are more durable. They are typically made of polymer or rubber, with fibers from other materials added for reinforcement. These belts are a good replacement for leather belts and offer many benefits. They are durable, offer excellent temperature and oil resistance, and are easy to use. If you’re considering replacing your current belt, consider buying a replacement belt made of the same material.
Most classical V-belts are used individually and come in A and B sizes. They are rarely used in single-belt drives. Buying several A or B belts instead of 1 C belt can save money. The narrow V-belts also provide higher power ratings. This is due to their narrow profile, which places more of the reinforcing cord under the sheave. Narrow V-belts are ideal for heavy duty applications.
When you’re replacing an existing V-belt, you’ll need to measure its top width and circumference. Once you’ve determined these parameters, you’ll be able to select the right replacement belt. Make sure to take measurements of the belt’s dimensions and top width before ordering. Using these measurements will help you determine the best size for your new belt. You’ll be able to tell whether you need a larger or smaller belt after measuring the top width and circumference.
If you’re looking to replace your leather belt with a belt made of synthetic material, a Classical V-belt may be the right choice. Classical V-belts are available in many materials and are more durable than leather. And because they are so versatile, they are the perfect replacement for your current belts. You’ll be glad you did. So, don’t be afraid to experiment with this type of belt. They’ll work well in any setting, including heavy equipment.
When buying a Classical V-belt, be sure to check the dimensions and type of belt you choose. These are available in notched or cogged designs. Notches are a great way to reduce bending stress. Notches also help dissipate heat from the belt, a major factor in premature belt failure. Notched V-belts are designed to balance a combination of flexibility and tensile cord support. They are spaced properly to minimize cracking and undercord damage.
Unlike leather belts, Classical V-belts are made of synthetic materials. They are easy to install, have a wide range of sizes, and come in light to heavy-duty varieties. The V-belt’s trapezoidal shape helps it track in the grooves of pulleys and prevents it from slipping while in use. It also helps in reducing power loss, since it’s easier to grip the pulleys than leather.
Narrow v-belts are more efficient
There are 5 basic types of V-belts. Their differences in cross-sectional size and power transmission make them superior to multiple single v-belts. The diagram below shows these types and how each differs from 1 another. The included angle of each belt is 40 degrees. The lower number indicates the more efficient version. Narrow V-belts are generally less expensive. Narrow v-belts are generally more efficient than wider belts.
There are several factors that influence a V-belt’s efficiency. Although the efficiency is high when a new belt is installed, the efficiency can drop to the low nineties. However, these belts are relatively resilient, and even with lower efficiency can function properly. Even if the efficiency of a V-belt is lower than it could be, it will still function. In fact, the higher the efficiency, the more energy it will save.
The first is the type of pulley. A narrow V-belt is more flexible than its wider counterpart. The belt pitch diameter is 32deg or 38deg. In addition, the belt can be cogged for added flexibility. In this way, the belt will not touch the bottom of the groove, but will only contact the inclined flanks. Without this wedge effect, the belt’s total friction force is higher. This means that it can transfer higher forces.
While a V-belt looks like a glorified rubber band, it has undergone tremendous technological development since it was first used in 1917. Synthetic rubber compounds and other cover materials have replaced rubber in the belt. New construction methods, tensile cord improvements, and cross-section profiles have resulted in a confusing variety of V-belts. Their differences, however, are based on the type of application for which they’re used.
Another type of V-belt is the raw edge variety. This type of belt is commonly used in manufacturing facilities. This type of belt requires less energy to operate. The raw edge also resists hardening. This is important since unmatched flexibility results in a smooth belt. Also, notched V-belts reduce vibration by 80%. Further, angular misalignment increases the risk of premature failure of a V-belt.
These belts differ in their overall design. While conventional V-belts are more common, narrow V-belts are more efficient and versatile. They are made of different types of rubber and reinforcements, which combine to create a trapezium-shaped cross-section. They can handle fractional loads and even 500 horsepower. Furthermore, their durability is largely dependent on their ability to withstand poor operating conditions.
Double-sided v-belts have unique features. These belts are used in applications with multiple pulleys. They can be operated clockwise or counter-clockwise. They can also be used to drive around multiple reverse bends. Further, they are more efficient and quieter than their counterparts. Finally, double-sided v-belts have 2 compression cores. The tension cord runs through both sections.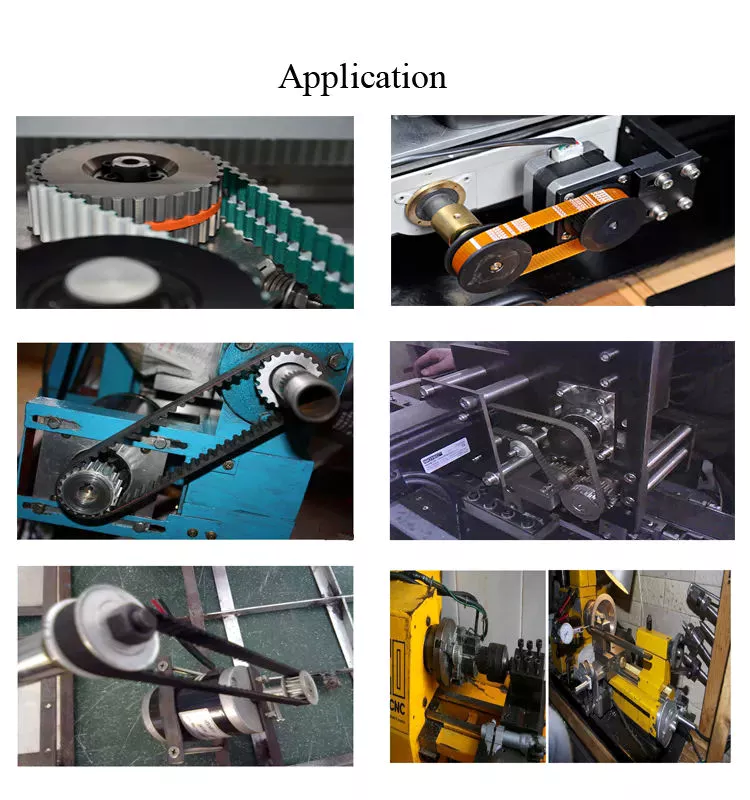
Double cogged v-belts increase lateral rigidity to reduce belt whip
A double cogged v-belt is a hybrid of a traditional double versus a cogged vee-belt. These belts are useful for applications that require a large amount of flexibility without compromising durability. The double cogged design also allows the belt to follow a serpentine path. The varying dimensions of a double cogged v-belt depend on manufacturer standards.
A v-belt is measured by defining the centerline, the inside length of the v-belt, and the pitch line, which is the distance between the top and bottom sides of the trapezium. The width and height of a v-belt are defined by its cross-section. Each cross-section is given a different designation, including the width and height.
A standard V-belt is a v-belt with a fabric cover. It provides firmness in a smaller space and is less prone to belt whip when used in heavy-duty applications. Its slim profile and light gauge tensile cord make it suitable for many industrial applications. The standard length of a double cogged v-belt varies from 530 to 3,000 mm.
Single cogged v-belts are commonly used in manufacturing machines that operate in close proximity to 1 another. Single cogged v-belts increase lateral rigidity and reduce belt whip. They are also ideal for heavy-duty applications, such as in mining or quarrying. Double cogged v-belts also increase lateral rigidity to minimize belt whip.
The elastomer core of a v-belt is surrounded by tension cords. These tension cords are embedded into the rubber compound, creating a composite structure that provides a high degree of shock resistance and flexural strength. The tension cords are often made of steel, polyester, or aramid fibers. This material makes it much stronger and more durable.
A double cogged v-belt is a highly rigid option for applications where lateral rigidity is an important concern. The double cogged design also increases lateral rigidity to reduce belt whip and enhances power transmission efficiency. Double cogged v-belts also offer positive slip-proof engagement. These belts are also easier to maintain, require less maintenance, and require no lubrication.


China manufacturer Timing Belt Tensioner Pulley OEM No.: 0463633 for CZPT 240 P242 P244 B 19 a B 21 a B 21 E CZPT Tensor De Alternador /Tensor De Correa near me factory
Product Description
Product spections :
| Tensioner Pulley | 0463633 04636338 463633 4636338 CZPT 240, Break Kombi 340-360 Saloon II Estate, , 965 P242 P244 P245 | Outer diameter [mm]: 47,00 mm |
| Width [mm]: 29,00 mm |
| 1995 | Volvo | 940 | Base Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 1995 | Volvo | 940 | Base Wagon 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 1995 | Volvo | 940 | T Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Turbocharged |
| 1995 | Volvo | 940 | T Wagon 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Turbocharged |
| 1994 | Volvo | 940 | Base Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 1994 | Volvo | 940 | Base Wagon 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 1994 | Volvo | 940 | T Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Turbocharged |
| 1994 | Volvo | 940 | T Wagon 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Turbocharged |
| 1993 | Volvo | 940 | Base Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 1993 | Volvo | 940 | Base Wagon 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 1993 | Volvo | 940 | T Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Turbocharged |
| 1993 | Volvo | 940 | T Wagon 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Turbocharged |
| 1992 | Volvo | 740 | Base Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 1992 | Volvo | 740 | Base Wagon 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 1992 | Volvo | 740 | T Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Turbocharged |
| 1992 | Volvo | 940 | T Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Turbocharged |
| 1992 | Volvo | 940 | T Wagon 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Turbocharged |
| 1991 | Volvo | 740 | Base Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 1991 | Volvo | 740 | Base Wagon 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Naturally Aspirated |
| 1991 | Volvo | 740 | T Sedan 4-Door | 2.3L 2316CC l4 GAS SOHC Turbocharged |
Description :
1. The tensioner is a belt tensioner used in the automobile transmission system. The tension pulley is mainly composed of a fixed shell, a tension arm, a wheel body, a torsion spring, a rolling bearing and a spring sleeve. It can automatically adjust the tension force according to the different tightness of the belt to make the transmission system stable, safe and reliable.
2. The main function of the tensioner bearing is to support the mechanical rotating body.
3.Reduce the friction coefficient during its movement and ensure its rotation accuracy.
4.Change sliding friction into rolling friction.
Tips For Replacing a Belt Tensioner
When replacing a serpentine belt or automatic tensioner, you will need a special tool. This tool has a long, flat extension handle that allows you to place a socket onto the bolt and flats on the tensioner arm. The following are some tips to follow when replacing the belt or tensioner on your vehicle. To replace your belt or tensioner, you should start by checking the tensioner’s lubrication.
Serpentine belt
If you notice that the power steering or air conditioning are not working, you should check the serpentine belt tensioner. A malfunctioning serpentine belt tensioner can lead to a host of other issues. The belt may stretch, which can be caused by several factors. Over time, serpentine belt tensioners can also get worn down. Additionally, they can have a variety of other problems, including rust or dirt in the housing.
You can replace your serpentine belt by following the instructions found on your vehicle’s manual. Some tensioners attach to the engine via a single bolt. To remove and replace the belt, remove the old unit and the retaining bolt. Locate the locking pin in the engine and place the new tensioner over it. Use a torque wrench or hand tool to tighten the bolts. When installing the new tensioner, be sure to line up the mounting bolt holes with the mounting bolts. Once the tensioner is installed, test the tension by ensuring that the gauge is above the ribs. If it slides down, it is time to replace the tensioner.
Before you begin the process of replacing your serpentine belt, be sure to park your vehicle in a level area. Turn off the engine and chock both rear wheels before starting the process. Using a diagram from your vehicle’s repair manual can make the process easier, especially if you are a beginner. You can draw it in your hand, or refer to a repair manual to find out the exact location of the tensioner pulley.
If you notice that the belt is slipping or squealing while driving, it may be time to replace the serpentine belt tensioner. A worn-out belt can cause the belt to slip and can cause power steering, air conditioning, and alternator malfunctions. You should also check the belt tensioner regularly. The motor may stall or make a loud noise. These are all signs of worn-out serpentine belt.
A serpentine belt uses less space in the engine than a V-belt. It also provides more tension for the serpentine belt, which prevents it from running hot and squealing. Serpentine belts are manufactured to last for several hundred thousand miles. They are a must-have item for your car! So be sure to keep it maintained and properly adjusted! Then, you can be sure to have your car running smoothly and safely.
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should replace your serpentine belt tensioner. A serpentine belt tensioner is a simple self-10sioning device that is mounted on the front of the engine. These devices are usually easy to replace and are not complicated to install. You can find 1 at any parts store or online. When the time comes to replace your serpentine belt, don’t hesitate to get the parts you need from a local auto part store.
Idler pulley
The idler pulley and the belt tensioner are essential components of your car’s drivetrain. If any 1 of them fails, all of them must be replaced. This is because they were manufactured at the same time and most likely have the same number of miles on them. As a result, they can all fail within a few thousand miles of each other. Here are some of the symptoms that you should look for when inspecting your idler pulley or belt tensioner.
Idler pulleys are a common part of most cars. They play a vital role in the operation of the belt system by directing the belt’s path and providing additional contact with the pulley. The idler pulley is also responsible for turning the cooling fan in an air-cooled Corvair engine. Because of these functions, idler pulleys are often replaced with idlers that differ in size.
Idler pulleys are small, 2 to 4 inches in diameter and mounted on the front of the engine block. Their purpose is to create a constant amount of tension on the drive belt. When the idler pulley is worn out, the accessory drive belt may experience excessive vibration and squealing noises. You may wish to replace it as soon as possible. You can do so at AutoZone.
A worn or damaged idler pulley will require a replacement. The belt itself will not fall off the car unless the idler pulley is damaged. A squealing sound can be a sign of a broken spring. Alternatively, a mechanic can recommend a replacement based on the condition of the idler pulley. In most cases, idler pulleys are more durable than the belts and are therefore recommended for replacement.
You can also notice that the idler pulley is slipping or causing excessive noise. Its constant rotation wears the idler pulley and reduces the tension of the belt. This causes the belt to slip and may even tear off the engine. Ultimately, this could result in stalling. And if you notice the engine belt squealing or making excessive noises, you should consider replacing it.
An idler pulley for a belt tensioner are often confused. Though both of them are used in the same application, they differ in many ways. The tensioner is the 1 that receives pressure from the belts and moves them. The idler pulley is not attached to an adjustable bolt, and it can cause unusual noises. It might even make squealing or odd noises.
Spring tensioner
A spring belt tensioner is a solution to a loose belt. It features a strong torsion spring that reduces slack. These devices are designed to fit up to 6mm wide belts. They are highly reliable and durable. They are also suitable for applications where the engine speed is often fluctuating. Here’s how you can choose the best 1 for your vehicle. The spring in the tensioner should be in the proper position to keep the belt taut and free of slippage.
The RunRight tensioner is a durable, high-quality product that uses aluminum alloy. Its elastomeric inserts rely on highly elastic natural rubber for good shape memory and durability. Spring tensioners are easy to install and maintain. They are designed for both axial and helical drives. They feature detailed technical drawings and 3-D models to help you determine the best 1 for your application. To choose a spring tensioner, visit our website.
A worn bushing in the tensioner pulley or a loose pivot arm can result in excessive noise, vibration, and premature belt failure. In addition, worn springs cannot maintain proper tension. Over time, they lose tension. The pulley arm itself can also become damaged, preventing it from rotating properly. If these problems occur, you’ll need to replace the spring tensioner. If you don’t see any signs of wear, check your mounting bracket and tensioner.
A worn pivot bushing can cause the tensioner arm to misalign, leading to excessive back and forth sway. It may also cause the tensioner to jam, which means the belt is too long or too short. If you notice excessive wobble, you should replace the spring tensioner. A faulty tensioner may also be causing excessive oscillation in the pulley. To determine if the spring tensioner is too weak or jammed, check the belt’s length by using a breaker bar or socket with a long handle ratchet.
When it’s time to replace your serpentine belt, don’t forget to replace the belt tensioner. The tensioner protects other components from premature failure. It is a relatively inexpensive repair. It should be replaced as part of a larger multi-ribbed belt. It also provides protection for other components of the drive system. In addition to its protection and performance, the tensioner is inexpensive and relatively easy to replace.
It’s vital to check the tensioner and idler pulleys to make sure the system is aligned properly. If they don’t align, the belt will slip and cause premature wear. Alternatively, the tensioner may have too much tension, overloading the shaft bearings and causing premature failure in other parts. You should also check the idler pulleys for noise as well, since these are engine-driven accessories.

